Split a string to a table using T-SQL
There is no built-in function to split a delimited string in Microsoft SQL Server, but it is very easy to create your own. The following Table-Valued Function (TVF) will split a string with a custom delimiter, and return the results as a table. This means you can easily use the output directly in a JOIN with some other data.
CREATE FUNCTION [dbo].[Split]
(
@String NVARCHAR(4000),
@Delimiter NCHAR(1)
)
RETURNS TABLE
AS
RETURN
(
WITH Split(stpos,endpos)
AS(
SELECT 0 AS stpos, CHARINDEX(@Delimiter,@String) AS endpos
UNION ALL
SELECT endpos+1, CHARINDEX(@Delimiter,@String,endpos+1)
FROM Split
WHERE endpos > 0
)
SELECT 'Id' = ROW_NUMBER() OVER (ORDER BY (SELECT 1)),
'Data' = SUBSTRING(@String,stpos,COALESCE(NULLIF(endpos,0),LEN(@String)+1)-stpos)
FROM Split
)
GOTo use Split(), just call it in a SELECT as you would a normal table:
DECLARE @DelimitedString NVARCHAR(128)
SET @DelimitedString = 'Duckman,Cornfed,Ajax,Charles,Mambo'
SELECT * FROM dbo.Split(@DelimitedString, ',')This will split the string and output an ordered table with each value:
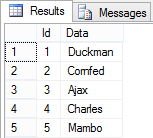
The output table has the column “Id” containing the original index of the value in the string. The column “Data” contains each string value. You can also use Split() directly in a join with another table like this:
SELECT Users.[Name] FROM dbo.Users
INNER JOIN dbo.Split(@DelimitedString, ',') AS split
ON Users.[Name] = split.[DATA]Notice that Split() uses common table expressions (CTE), a feature added to T-SQL in Microsoft SQL Server 2005, and will not work on earlier versions.